

Updated · Jan 10, 2024
Updated · Aug 15, 2023
Raj Vardhman is a tech expert and the Chief Tech Strategist at TechJury.net, where he leads the rese... | See full bio
Girlie is an accomplished writer with an interest in technology and literature. With years of experi... | See full bio
A proxy server is an intermediary between various entities on the web. While it has several applications, traffic filtering, network security, and site caching are the most common.
Proxy servers can be either forward or reverse. Both proxies improve system performance and safety in different ways and for various reasons.
Understanding the distinctions between the two is critical for creating and putting together scalable and secure systems.
Read further to learn the main differences between the two concepts.
The primary distinction between the two proxies is the purpose they serve.
A forward proxy adds an extra layer of security for the user. On the other hand, a reverse proxy is designed to keep web servers stable and performant.
Before digging deeper into their differences, it's critical to understand each proxy's definitions and applications.
Proceed through the following sections for a more in-depth understanding of forward and reverse proxies.
A forward proxy, sometimes known as a proxy server, stands between a client and the internet. When a client device attempts to access a specific web resource, it first contacts the forward proxy server.

A proxy server searches the Internet for websites, servers, and services on your behalf, and Windows 10 users can access the Internet using this system.
The configuration parameters of the forward proxy will decide whether or not a request is permitted. If granted, the proxy server will obtain the required Internet data and provide it to the client.
The client does not know the request was processed through a proxy server because the interaction appears direct.
Smartproxy is a top-rated proxy provider trusted by many. Its 40 million+ proxies from 195+ locations help bypass CAPTCHAs, geo-blocks, and IP bans. It offers a free trial and has a high rating of 4.7 on Trustpilot with 89% 5-star ratings, making it one of the best in the industry.
Forward proxies are often used to regulate internet access, censor content, or provide the client with anonymity.
They may also improve resource access by caching frequently accessed material. Proxy servers offer numerous purposes as your online middleman.
Here are some of the most common applications for a forward proxy server:
Since IP addresses serve as a base for a user's online identity, masking your IP address is the key to online anonymity.

The proxy server hides the client's IP address and other identifying information from the destination server when they connect to the internet via a forward proxy.
This adds extra security and privacy, making it more challenging for internet thieves to track the client's activity.
Caching describes keeping several copies of data or files in a temporary storage location, or "cache," to enable quicker access.
The DNS cache is a temporary database that Windows keeps of all successful and unsuccessful website visits and records previous DNS lookups that the operating system or web browser stores.
When users launch an app or visit a website, multimedia, including photos, files, and scripts, are immediately cached on their device.
This minimizes latency, the time it takes for data to move over the internet.
|
⚠️Warning: Cookies, browser history, passwords, and other information may be stored in cache memory. Always be careful and vigilant to prevent unauthorized access to your stored data. |
A forward proxy may detect illegitimate corporate network devices, like shadow IT.
According to Microsoft, 80% of employees use applications that have yet to be examined and may violate the company's security and compliance regulations.
A proxy can help you navigate these risky apps, configure policies to identify new problematic apps, and effectively block unsanctioned apps.
|
💻Definition Shadow IT refers to using technology, including software and services, without explicit approval or knowledge from the organization’s IT department. Organizations need to address the issue of shadow IT to maintain network security and enforce compliance. |
Organizations often use forward proxies to limit users' access to certain websites or online material based on predetermined policies.
It ensures regulatory compliance by intercepting and analyzing client requests, adding a layer of security.
If you watch anything online, geo-blocking restricts access to specific content based on a user's location.
Before the popularity of VPNs, proxy servers were the most popular way to access geo-restricted content without paying a dime.
|
👍Helpful Article: VPNs outperform proxy servers in some cases. To help you decide which one to use, check out Techjury’s article on Proxy vs. VPN. |
From ransomware to phishing, many typical cyber dangers may be spotted early with the correct tools and methods.
Forward proxies can mitigate risks and maintain a secure online environment when strategically deployed and configured.
|
👍Helpful Articles: To learn more about internet phishing and ransomware, check out Techjury’s article on phishing and ransomware statistics. |
The web scraping process involves using software or tools to gather information from web pages in a structured manner.
This is usually done for various purposes, such as data analysis, market research, monitoring prices, content aggregation, etc.
Forward proxies are integrated into web scraping to enhance privacy, improve reliability, and overcome limitations imposed by websites.
|
👍Helpful Articles: Google Chrome enables users to set up their proxy servers. You may also customize it to meet your particular needs. |
Unlike a standard proxy server, a reverse proxy safeguards servers.

A reverse proxy receives requests from clients on behalf of the servers behind it. In effect, a forward proxy conceals clients' identities, whereas a reverse proxy conceals the identities of servers.
|
|
👍Helpful Article: Suppose you've already decided to employ a reverse proxy. Check out Techjury's guide on how to set up a reverse proxy. |
Protecting backend servers from harmful traffic is one of the many uses for reverse proxies.
If you've ever encountered a "504 Gateway Time-Out" error, the reverse proxy informs you that the backend server is inaccessible.

Some of the most common reasons why it’s important to set up a reverse proxy server include the following:
When confronted with massive traffic, single servers may suffer from degrading performance and increasing request latency.

Reverse proxies divert web traffic to other servers if one of the primary servers becomes overcrowded or otherwise inoperable.
This is essential for websites that utilize multiple backend servers.
Reverse proxies store content online to speed up page loads worldwide. The scalability of this process is ensured via several reverse proxies located in strategic locations.
Suppose a user in Asia tries to access a North American web server using a reverse proxy. In that case, the user may be redirected to a more geographically convenient reverse proxy server in Asia.
Every time a website is browsed, traffic is routed to nearby servers rather than the website's origin server, which speeds up content loading and guarantees excellent availability despite growing demand.
Decrypting and encrypting messages for each client can be costly for an origin server.
As a solution, a reverse proxy can be set up to do the encryption and decryption, reducing the load on the server.
The FBI's Internet Crime Complaint Center (IC3) stated in its most recent report that the bureau received over 800,000 complaints linked to cybercrime in 2022, with damages totaling over $10 billion.
When using a reverse proxy, the IP address of the primary server is concealed, making it difficult for hackers to target the server directly.
Instead, hackers will be limited to targeting the reverse proxy.
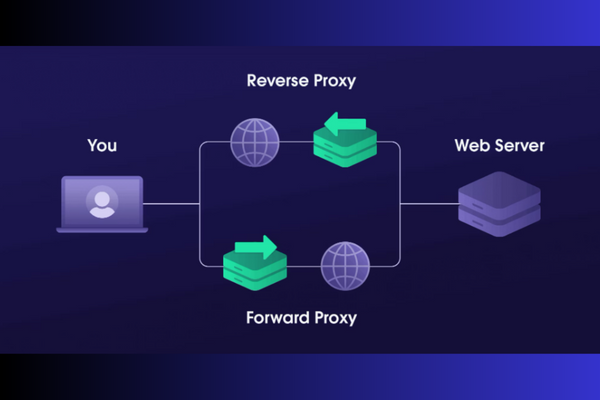
Since you're already aware of the general characteristics, locations, and functions of a forward proxy and a reverse proxy, it's time to dive into what sets them apart.
A forward proxy guarantees that websites never connect with a user directly. At the same time, a reverse proxy prevents users from communicating directly with a back-end server.
Forward proxies connect a client to the internet, while reverse proxies direct internet traffic to a web server.

By caching frequently visited sites, forward proxies minimize web server load and enhance response time.
Although reverse proxies can perform the same function, caching is handled by a server that is physically closer to the user.
While a reverse proxy protects the server's identity, a forward proxy does the same for the client.
A reverse proxy can make it easy to scale online applications by dynamically adding and removing servers. Forward proxies do not provide any means of scalability.
Only a reverse proxy can distribute incoming traffic across multiple servers between the proxies.
A forward proxy is easy to configure and maintain, while a reverse proxy is more complex due to its complicated capabilities.
Usually, forward proxies do not frequently terminate SSL/TLS connections. However, a web server can delegate the task of terminating SSL/TLS connections to a reverse proxy.
Forward proxies can redirect traffic to various servers according to predetermined rules.
Reverse proxies may also execute routing based on multiple factors, such as the URL path, HTTP headers, or geographic location.
An example of a forward proxy is Squid, although there are also Tor, PHP-Proxy, and CGI-Proxy.
On the other hand, Nginx, Apache, HAProxy, Istio, and Linkerd are all reverse proxies.
Here is a quick recap of the key distinctions we've covered:
|
Forward Proxy |
Reverse Proxy |
|
|
Functionality |
Conceals the client’s identity. |
Conceals servers’ identities. |
|
Direction of Traffic Flow |
Directs traffic from a client to the internet. |
Directs internet traffic to a web server. |
|
Caching |
Caching occurs between the client and the origin server. |
Caching is handled by a server physically close to the user. |
|
Security |
Protects the client. |
Protects the servers. |
|
Scalability |
Not applicable. |
It makes it easy to scale online applications. |
|
Load Balancing |
Not applicable. |
Distributes incoming traffic across multiple servers. |
|
Configuration |
Easy to configure and maintain. |
Complex due to its complicated capabilities. |
|
SSL/TLS termination |
Not applicable. |
Can delegate the task of terminating SSL/TLS connections. |
|
Routing |
Redirect traffic to various servers according to predetermined rules. |
It may also execute routing based on multiple factors, such as the URL path, HTTP headers, or geographic location. |
|
Examples |
Squid, Tor, PHP-Proxy, and CGI-Proxy |
Nginx, Apache, HAProxy, Istio, and Linkerd |
Forward and reverse proxies are utilized for different tasks and cannot be considered the same.
Both proxies are essential components of a well-designed network, but they do different things and provide other benefits.
To efficiently manage and secure network traffic, it is crucial to get an understanding of their distinctions.
Reverse proxies are particularly effective in managing requests on the server side, which in turn improves network speed and reliability.
Suppose your primary worry is privacy and security when browsing the internet, accessing geo-restricted information, or scraping—a forward proxy is already enough.
|
👍Helpful Articles: If you plan to use a proxy server in the future, check out the following articles from Techjury: |
A VPN is similar to a forward proxy in that it routes user traffic through its servers; however, VPNs route traffic through encrypted tunnels, which may better protect user data.
No, NAT alters network packets transparently, whereas a reverse proxy accepts and terminates network connections before re-transmitting requests to the destination.
No, it's the other way around. A reverse proxy is a type of firewall.
Using a proxy server is advisable. Without a proxy server, hackers can easily access your IP address, which they may exploit to attack your computer or network.
Your email address will not be published.
Updated · Jan 10, 2024
Updated · Jan 09, 2024
Updated · Jan 05, 2024
Updated · Jan 03, 2024





